RBGPF
-1.0000

Cloaked in darkness and mystery, the creatures of the deep oceans exist in a world of unlikely profusion, surviving on scant food and under pressure that would crush human lungs.
This extremely hostile environment, which will come under the spotlight at a major United Nations oceans summit in Lisbon this week, has caused its inhabitants to develop a prodigious array of alien characteristics and idiosyncratic survival techniques.
A vast assortment of animals populate the sunless depths, from the colossal squid, which wrapped its tentacles around the imaginations of sailors and storytellers, to beings with huge cloudy eyes, or whose bodies are as transparent as glass.
And the angler fish, with its devilish looks illuminated by a built-in headlamp, showing that the deep dark is alive with lights.
- 'Incredible' creatures -
Until the middle of the 19th century, scientists believed that life was impossible beyond a few hundred metres.
"They imagined that there was nothing, because of the absence of light, the pressure, the cold, and the lack of food," Nadine Le Bris, a professor at Sorbonne University, told AFP.
Between 200 and 1,000 metres (650 to 3,300 feet), the light fades until it vanishes completely, and with it plants; at 2,000 metres the pressure is 200 times that of the atmosphere.
From the abyssal plains to the cavernous trenches plunging deeper than Everest is high, aquatic existence continues in spectacular diversity.
"When people think of the deep sea they often think of the seafloor," said Karen Osborn of the Smithsonian's Natural History Museum.
"But all that water in between is full of incredible animals. There is a ton of life."
These open water inhabitants face a formidable challenge: they have nowhere to hide.
"There's no seaweed to hide in, no caves or mud to dig into," said Osborn.
"There are predators coming at them from below, from above, from all around."
- Masters of disguise -
One tactic is to become invisible.
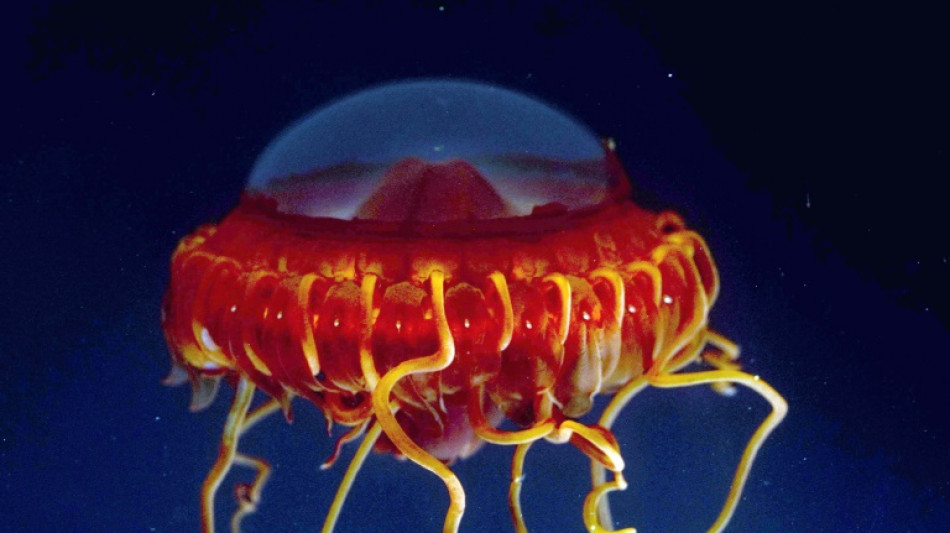
Some creatures are red, making them difficult to distinguish in an environment where red light no longer filters through.
Others render themselves transparent.
Take the transparent gossamer worm, which ranges in size from a few millimetres to around a metre long and shimmies through the water by fluttering its frilly limbs.
"They look like a fern frond," said Osborn.
"They're beautiful animals and they shoot yellow bioluminescent light out of the tips of their arms. What could be better than that."
Bioluminescence is particularly common among fish, squid, and types of jellyfish, according to the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, which says around 80 percent of animals living between 200 and 1,000 metres produce their own light.
This chemical process might be helpful for defence, reproduction or to find food -- but no one knows for sure why so many creatures have evolved it, says NOAA.
- "Sea snow" -
With no plants around and animals scattered in the vastness doing their utmost to disappear, creatures in the ocean depths often have a hard time finding a live meal.
"If you happen to get lucky and hit a patch of your food, bingo! But you may not see another one for three weeks," said Osborn.
Another option is to feast on the dead.
Organic particles from the surface waters -- disintegrated bodies of animals and plants, mingling with fecal matter -- drift down in what is known as "marine snow".
This cadaverous confetti forms part of a process that sequesters carbon dioxide in the ocean depths.
It is also a lifeline for many deep sea animals, including the blood red vampire squid which, contrary to its reputation, peacefully hoovers up marine snow.
When giants like dead whales sink to the seabed, they are swiftly reduced to bone by scavengers.
- Final frontier -
With most of the oceans still unexplored, it is often said that we know more about the surface of Mars than we do about the seafloor on our own planet.
But unlike outer space, scientists keep finding life even under the most hostile of conditions.
Like the searing hydrothermal vents at the cracks between oceanic plates that spew chemical compounds such as hydrogen sulphide.
Microorganisms use this to create organic matter via "chemosynthesis", like plants use the sun for photosynthesis, which in turn feeds "exuberant" ecosystems, said Pierre-Marie Sarradin, head of the Deep Ecosystems department at the French research agency Ifremer.
These hydrothermal springs were totally unknown until the 1970s.
Scientists have so far identified some 250,000 marine species, though there could still be at least a million to be discovered.
Could there be an elusive sea monster lurking in the depths? Despite measuring more than 10 metres in length the colossal squid has only very rarely been seen.
"I don't think we're going to find a megalodon," said Osborn, referring to the giant ancestor of the shark.
Humans may not have explored much of the deep seas, but they have left their mark, via global heating, overfishing and pollution.
Oceans are acidifying as they absorb more and more CO2, there is a growing prevalence of "dead zones" without oxygen, while microplastics have been found in crustaceans at a depth of nearly 11 kilometres in the Mariana Trench.
Food reaches the bottom in smaller quantities.
Nadine Le Bris said species that "already live at the limits in terms of oxygen or temperature", are already "disturbed".
U.Siddiqui--DT